SAP Transportation Management
- 4 - 5 weeks
- 30 Hours
- 2400+ Student Enrolled

Live Instructor Online Training
Learn From SAP Experts
- Certified SAP Experts for more than 10+ years.
SAP TM Online Training
Have Queries? Ask our Experts
+91 9922848898
Course Overview
Welcome to a transformative journey in logistics excellence! Your path to becoming a SAP Transport Management (SAP TM) expert begins with our SAP TM Certification course. Take advantage of our in-depth SAP TM module training to gain the knowledge and abilities required for effective transport management.
With our professionally conducted SAP TM training, you can unlock the potential of SAP Transportation Management Systems. Our curriculum covers everything, from basic ideas to sophisticated methods, making sure you're ready for SAP TM certification. If you're interested in navigating the complexity of this intricate system, let's explore the SAP Transport Management system to discover more about its architecture, features, and best practices. Our carefully designed SAP TM courses are designed to provide you the knowledge and practical skills required to succeed in SAP TM.
SAP TM fullform is SAP Transportation Management is a comprehensive logistics solution that optimizes and manages end-to-end transportation processes for businesses. It facilitates efficient planning, execution, and monitoring of shipments while integrating with other SAP modules for seamless operations. SAPTM module enhances visibility, cost control, and customer satisfaction in supply chain logistics.
SAP TM (Transportation Management) is a module within the SAP suite that helps organizations manage and optimize their transportation processes. It covers areas such as planning, execution, freight management, and carrier collaboration. SAP TM enables businesses to efficiently plan and monitor shipments, select optimal routes, and track deliveries. It enhances visibility, reduces transportation costs, and ensures timely and accurate deliveries to customers and our SAP TM training has it all.
In Technical Terms: SAP TM (Transportation Management) is a comprehensive solution within the SAP ecosystem designed to facilitate strategic transportation planning, execution, and monitoring across supply chain operations. It encompasses a range of functionalities, including carrier selection, route optimization, freight cost calculation, and real-time tracking. SAP TM leverages master data such as transportation lanes, carriers, and freight rates to ensure optimal resource utilization and cost efficiency.
The solution integrates with various SAP modules, like Materials Management (MM), Sales and Distribution (SD), and Warehouse Management (WM), to ensure seamless coordination across logistics processes. It employs advanced algorithms for load consolidation, carrier collaboration, and tendering processes to streamline transportation execution. By offering real-time visibility into shipment statuses, SAP TM module enables proactive issue resolution and enhances customer satisfaction.
SAP TM also supports various transportation scenarios, such as domestic and international freight, multi-modal transportation, and cross-border customs compliance. It plays a pivotal role in enhancing supply chain efficiency, reducing transportation costs, and maintaining compliance with industry regulations. Through its integration with SAP's broader technology stack, SAP TM empowers organizations to orchestrate complex transportation networks with precision and agility.
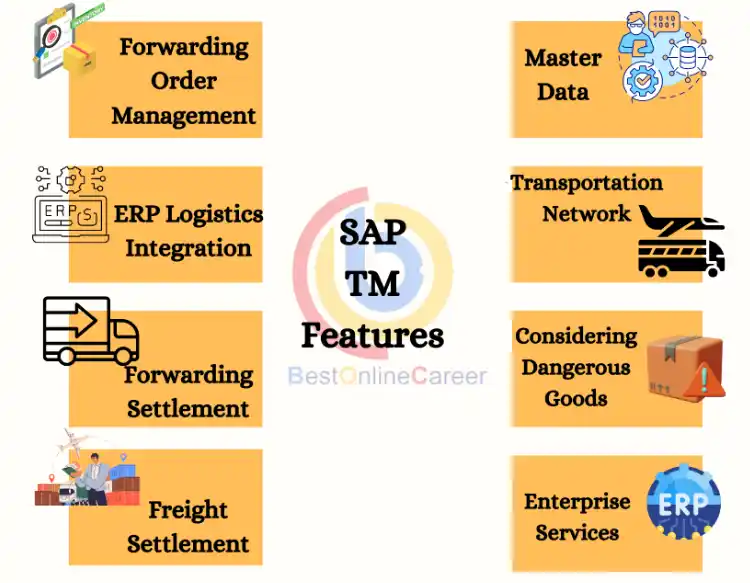
1.Forwarding Order Management: Forwarding Order Management systems are crucial in logistics and shipping operations. They streamline the entire order-to-shipment process, encompassing order creation, carrier selection, tracking, and delivery confirmation. This software optimizes resource allocation, enhances order accuracy, and improves customer service by providing real-time visibility into shipment status. It also supports order consolidation, reducing shipping costs.
2.ERP Logistics Integration: ERP Logistics Integration is a fundamental component of modern business operations. It bridges the gap between an organization's Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system and its logistics functions. By seamlessly connecting these systems, it allows for the exchange of critical information such as inventory levels, order processing, and financial data. This integration enhances decision-making, inventory management, and supply chain visibility, ultimately increasing overall efficiency and reducing errors.
3.Forwarding Settlement: Forwarding Settlement systems automate the complex financial aspects of freight forwarding and logistics. They facilitate accurate and efficient invoicing, billing, and payment processes for transportation services. These systems help companies avoid billing discrepancies, reduce manual labor, and ensure timely payments to carriers and service providers. They also provide detailed financial reporting, aiding in cost analysis and budgeting for logistics operations.
4.Freight Settlement: Freight Settlement is a critical component of logistics management. It involves the systematic process of reconciling and settling financial transactions related to freight transportation services. These systems help companies accurately allocate and track freight charges, ensuring that invoices are in line with contracted rates. Freight Settlement solutions reduce billing discrepancies, improve financial transparency, and support efficient payment processing for carriers and service providers. Additionally, they generate comprehensive reports for cost analysis, helping businesses optimize their transportation expenses.
5.Master Data: Master Data refers to the core data elements that are fundamental to an organization's operations. This includes information about products, customers, suppliers, and other essential business entities. Master Data Management (MDM) systems maintain the accuracy, consistency, and integrity of this critical data across the organization. By centralizing and standardizing master data, businesses can improve decision-making, streamline processes, and ensure data quality, ultimately enhancing overall efficiency and reducing errors.
6.Transportation Network: Transportation Network solutions play a pivotal role in supply chain and logistics optimization. These systems provide tools to map, manage, and optimize transportation routes and connections. By analyzing factors like distance, traffic, and vehicle capacity, transportation network software helps organizations select the most efficient routes and modes of transport. This leads to cost savings, reduced transit times, and improved customer service through on-time deliveries and reduced transportation-related emissions.
7.Considering Dangerous Goods: Handling dangerous goods involves compliance with stringent regulations and safety standards. Software and systems designed for managing dangerous goods ensure that these materials are stored, transported, and handled in accordance with legal requirements. They facilitate proper classification, labeling, and documentation of hazardous materials, minimizing risks to employees, the environment, and the public. Such systems also aid in emergency response planning and reporting, ensuring organizations meet their legal obligations while maintaining safety.
8.Enterprise Services: Enterprise Services encompass a broad range of software solutions and support that address various aspects of an organization's operations. These services are designed to enhance efficiency, scalability, and integration across different departments and processes. They include services like cloud computing, data analytics, cybersecurity, and application integration. By leveraging enterprise services, businesses can streamline operations, reduce IT complexity, and adapt more effectively to changing market demands. These services play a pivotal role in modernizing and future-proofing an organization's technology infrastructure.
.png)
1.Order Management: Order management is a crucial aspect of supply chain operations that involves the coordination and tracking of customer orders from initiation to fulfillment. It encompasses processes such as order entry, validation, allocation of inventory, scheduling, and monitoring order progress. Effective order management ensures accurate delivery and customer satisfaction while minimizing errors and delays. It often involves the integration of various systems to streamline the order-to-cash cycle, optimize inventory levels, and facilitate real-time visibility into order status for both customers and internal stakeholders.
2.Carrier Collaboration: Carrier collaboration refers to the strategic partnership between shippers and transportation service providers (carriers) to enhance the efficiency of freight transportation operations. It involves open communication, data sharing, and joint planning to optimize route planning, reduce empty miles, and minimize transportation costs. Collaborative efforts enable shippers to access a wider network of carriers and choose the most suitable options based on factors like rates, transit times, and capacity. Effective carrier collaboration can lead to improved service levels, reduced environmental impact, and better utilization of transportation assets.
3.Transport Planning: Transport planning involves the systematic process of designing and optimizing the movement of goods from origin to destination. It encompasses route optimization, mode selection, load consolidation, and scheduling to ensure efficient and cost-effective transportation. By leveraging advanced technologies and data analysis, transport planning aims to minimize transit times, reduce fuel consumption, and enhance overall supply chain performance. Successful transport planning considers factors such as traffic conditions, weather, delivery windows, and regulatory requirements to ensure on-time and safe deliveries.
4.Freight Procurement: Freight procurement refers to the process of sourcing transportation services from carriers or logistics providers to meet the shipping needs of a company. It involves activities such as negotiating rates, establishing contracts, and selecting carriers based on their capabilities, service levels, and cost-effectiveness. Effective freight procurement strives to strike a balance between quality and cost, taking into account factors such as freight volume, lane requirements, and market dynamics. By optimizing the procurement process, companies can achieve better rates, access reliable carriers, and enhance their overall logistics strategy.
5.Route Optimization: Route optimization is a critical component of logistics and transportation management that aims to streamline the movement of goods by identifying the most efficient and cost-effective routes for delivery. By utilizing advanced algorithms and real-time data, route optimization minimizes travel distances, reduces fuel consumption, and optimizes delivery schedules. This results in shorter transit times, lower operational costs, and improved customer satisfaction. Route optimization also considers factors such as traffic conditions, road restrictions, and delivery priorities to ensure timely and accurate deliveries.
6.Visibility and Tracking: Visibility and tracking solutions provide real-time insights into the location and status of shipments throughout their journey. By leveraging technologies like GPS, RFID, and IoT sensors, businesses can monitor their goods from origin to destination. This transparency enhances supply chain visibility, enabling accurate ETA predictions, improved inventory management, and effective response to unforeseen disruptions. Visibility and tracking systems also enhance customer satisfaction by providing customers with up-to-date information about their shipments.
7.Documentation and Compliance: Documentation and compliance management in logistics involve handling the required paperwork, regulations, and customs documentation associated with the movement of goods across borders or within a country. Ensuring accurate and timely documentation is essential to prevent delays at customs, avoid fines, and maintain smooth cross-border operations. Compliance management ensures adherence to international trade regulations, safety standards, and industry-specific requirements, reducing the risk of legal and operational complications.
8.Resource Management: Resource management involves optimizing the utilization of assets, including vehicles, equipment, and personnel, to ensure efficient logistics operations. Effective resource management minimizes downtime, reduces operational costs, and improves overall productivity. This includes activities like load planning, driver scheduling, maintenance scheduling, and capacity utilization optimization.
9.Global Trade Management: Global trade management encompasses the processes and systems required to manage international trade operations, including import/export compliance, customs regulations, tariff management, and trade agreements. It ensures that goods cross international borders smoothly while adhering to all legal and regulatory requirements. By automating and streamlining global trade processes, businesses can minimize delays, reduce costs, and mitigate risks associated with cross-border transactions.
10.Cost Management: Cost management in logistics involves controlling and optimizing the expenses associated with transportation, storage, and other supply chain activities. It includes activities like rate negotiation with carriers, cost analysis of different transportation modes, and identifying opportunities for cost reduction through process optimization. Effective cost management strategies contribute to increased profitability and competitive advantage by ensuring that logistics expenditures are in line with the value provided to customers.
There are several other Logistics Management Solutions available in the market, such as Kuebix TMS, Manhattan Associates TMS, Oracle Transportation Management (OTM), Descartes Systems Group, Trimble Transportation etc. While these solutions offer some benefits they still fall short when compared to SAP TM.
For instance, Kuebix TMS Offers a modular and scalable platform but May lack some advanced features required by larger enterprises. Manhattan TMS Focuses on omni-channel retail and distribution but Implementation and customization might require specialized expertise. Oracle OTM provides a comprehensive range of transportation and logistics tools but Implementation and integration with existing systems could be complex. Descartes Offers specialized logistics solutions but Could be cost-prohibitive for smaller organizations. Trimble Provides end-to-end visibility and optimization for transportation and logistics operations but Some users may find the interface overly complex.
Here's a comparison between SAP TM and other Logistics Management Solutions:
| Aspect | SAP TM | Other Logistics Management Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Comprehensive transportation management solution | Varies - Some offer specific functionalities for certain industries or logistics processes |
| Carrier Collaboration | Supports collaboration with carriers and partners | Collaboration features differ based on solution |
| Integration with ERP/MRP Systems | Integrated with SAP ERP/MRP modules | Integration options differ based on third-party systems and customizations |
| Analytics and Reporting | Advanced analytics and reporting features | Reporting capabilities differ based on solution |
| Cloud-Based Option | Available on SAP Cloud Platform | Some solutions are cloud-based, others offer both cloud and on-premises options |
| Industry Focus | Applicable to various industries | Some solutions cater to specific industries or sectors |
| Licensing Model | Proprietary licensing | Some solutions cater to specific industries or sectors |
SAP Transportation Management Architecture
- • Standalone SAP TM
- • Integrated SAP TM (SAP TM- SAP ERP)
- • Transportation Management E2E Cycle
SAP Transportation Management Master Data
- • Organization Master Data.
- • General Master Data
- • Transportation Network Master Data
SAP Transportation Management Requirement/Order Management
- • Order Based Transportation Request.
- • Delivery Based Transportation Request
- • Forwarding order Scenario
Transportation Capacity Management
- • Carrier Schedules
- • Port Schedules
- • Departure/Destination Rules
Freight Order Management is a pivotal component of modern logistics and supply chain operations. This comprehensive system is designed to efficiently handle and oversee the end-to-end process of shipping orders. From order creation to final delivery, it streamlines and optimizes every stage of freight management.
Freight Order Management systems facilitate the creation and modification of shipping orders, ensuring accuracy while reducing administrative errors. They empower businesses to make informed carrier selections, taking into account factors like cost, capacity, and service levels. These systems also excel in routing and scheduling, optimizing transportation routes to minimize transit times and reduce overall transportation costs.
Freight Order Creation: This component facilitates the efficient generation and modification of shipping orders, ensuring accuracy while minimizing administrative errors. It empowers users to initiate and manage freight orders, providing essential data such as shipment details, origin, destination, and cargo specifics. Freight Order Creation streamlines the initial steps of the shipping process, serving as a foundation for the entire logistics workflow.
Freight Order Stages: Freight Order Management includes a structured approach to handling shipments through various stages. It meticulously tracks the progress of each order, from initiation to final delivery. These stages typically include order entry, carrier selection, routing and scheduling, inventory management, and order tracking. Freight Order Stages optimize each phase of the logistics process, enabling precise monitoring and control over the movement of goods.
Freight Order Control: This aspect empowers organizations with the tools needed to oversee and manage shipping orders effectively. It provides real-time visibility into order status, inventory levels, and carrier performance. Freight Order Control automates billing and invoicing processes, reducing manual effort and errors. It ensures compliance with industry regulations, especially for handling hazardous materials, and offers cost analysis tools to monitor and control transportation expenses. Freight Order Control is central to maintaining operational efficiency, accuracy, and transparency within the logistics and supply chain management framework.
Transportation Execution/Control/Monitor. (Standalone TM and Integrated TM Perspective)
- • Transportation Execution.
- • Transportation Control.
- • Transportation Monitoring
Join us and expand your career in logistics through specialized SAP TM training. Maintain a competitive edge in the ever-evolving field of SAP transportation management — your journey to success starts here. You will acquire real knowledge and experience with our SAP TM training that goes beyond theoretical comprehension. We go above and beyond by offering a vibrant learning atmosphere where you can use your abilities in practical situations. Enroll now to take advantage of possibilities for professional development and to confidently enter a future where your SAP TM skills will open doors.
Job Opportunity
SAP TM Course Generates upto 60,000 - 65,000 jobs every year. (Source : indeed.com)
Online Corporate Training Course
- Curriculum aligned with latest industry trends
- Experienced and certified trainers
- Real-life scenarios
- Lifetime access to course material (pdfs, ppts and videos)
Recorded Video Online Training
- Updated course content
- Lifetime access to course content (videos and materials)
- Flexibility to learn anytime, anywhere
Instructor-Led Online Training
- Candidate pre-evaluation
- Certified and experienced trainers
- Email support and online query resolution
- 24/7 access to SAP Sandbox
Free Demo session
Study Material
Video recording
100% Job Assistance
Interview Preparation
The learning objectives for SAP Transportation Management (SAP TM) can vary based on the specific course or training program you're undertaking.
SAP TM Consultant, SAP TM Functional Analyst, Transportation Management Systems (TMS) Specialist, SAP TM Support Analyst, SAP TM Business Analyst, Logistics IT Manager, SAP TM Configuration Specialist, SAP TM Support Analyst, SAP TM Business Analyst, SAP TM Integration Consultant, SAP TM System Administrator
If the training is not taken by the candidate after paying the amount we do refund.
You have to install goto meeting/ training in your system.
We provide 24/7 server access where you can practice.
